As of February 2025, GDPR fines have reached a total of €5.6 billion across 2,295 violations. Whether it’s a massive data breach or a poorly handled consent form, the consequences of non-compliance are real and steep. However, many of these incidents can be avoided with one simple but essential investment: GDPR training for employees.
In this article, we’ll explore the biggest risk factors that lead to GDPR fines, the common mistakes that put organizations at risk, examples of serious violations, and how GDPR impacts different industries. Most importantly, we’ll show how these risks can be reduced through clear, engaging training methods.
Understanding the Gravity of GDPR Violations
If you’ve ever signed a contract with a European company, chances are you’ve also signed a data processing agreement. It’s become standard practice—whether it’s for sensitive services like healthcare or finance, or something as everyday as booking a vacation through a travel agency. For many, these forms feel like just another piece of paperwork. We glance at them, maybe roll our eyes, and move on.
But that clause is actually a legal safeguard. It protects businesses from potentially catastrophic GDPR violations that can cost thousands, millions, or even billions of euros (as we’ll see in several cases in this article). And more importantly, it protects you—the customer—from having your personal data handed off to unwanted third-parties.
Official EU Legislation on GDPR Fines
According to both the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) and the European Commission, enforcement actions against GDPR violations vary. Depending on the case, organizations can receive:
- A warning
- A temporary or permanent ban on processing
- Financial penalties
The two tiers of fines are based on the type and severity of the infringement:
Tier 1: Up to €10 million or 2% of annual global revenue (whichever is higher) for failures related to Articles 8, 11, 25–39, 42, and 43, concerning:
- Data controllers
- Processors
- Certification bodies
- Monitoring bodies.
Tier 2: Up to €20 million or 4% of global turnover (whichever is higher) for more severe breaches, such as:
- Violating core data processing principles (e.g., lawfulness, fairness, transparency)
- Failing to obtain valid consent
- Infringing on data subjects’ rights
- Transferring personal data to a third country or international organization without appropriate safeguards or approval from the European Commission that the country has adequate data protection laws.
Factors that Determine the Fine Amount
According to the European Commission, every GDPR fine should be effective, proportionate and dissuasive. The size and severity of GDPR fines depend on several things, including:
- The severity and duration of the violation
- Whether it was intentional or accidental
- The organization’s efforts to resolve or mitigate the issue
- Cooperation with the investigation
- Additional factors, such as past violations or compliance efforts
Most Frequent Causes of Fines
Similar to other cases of regulatory violations, various causes lead to GDPR or data protection violations, some stemming from improper training, miscommunication, or negligence, and some from pure intent or ignorance. Common triggers include:
- Lack of transparency with data subjects: Not clearly explaining how personal data is collected, used, or shared
- Mishandling of personal data: Storing, processing, or transferring data in ways that violate GDPR principles
- Weak or outdated security practices: Failing to implement modern protections against breaches or leaks
- Poor GDPR training for employees: Especially when companies treat it like a one-time seminar instead of an ongoing process
GDPR Fines by Violation Type
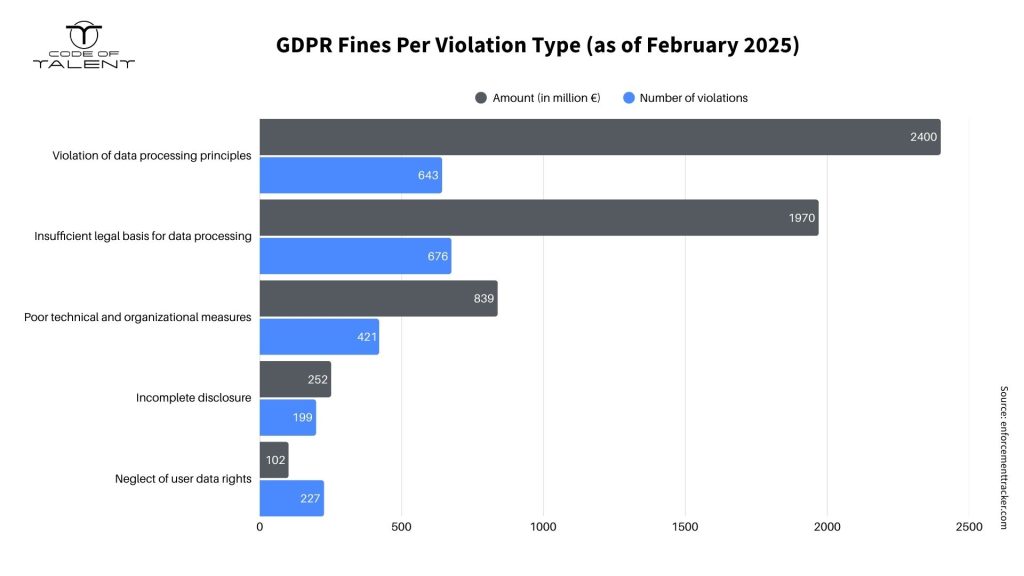
Non-Compliance with Data Processing Principles (Article 5 of the GDPR):
- Issues with fairness, transparency, and data minimization.
- Happens when too much data is collected or misused.
Failing to Fulfill Data Subjects’ Rights (Articles 12–22):
- Individuals’ rights like access, correction, and deletion are ignored.
- Happens when requests are delayed or denied.
Lack of Legal Basis for Data Processing (Article 6):
- Data is collected without a valid reason (e.g., consent or contract).
- Happens when companies don’t clearly document why they need data.
Uncooperative with Supervisory Authorities (Article 31):
- Failing to respond to data protection regulators.
- Happens when companies delay or ignore investigations.
Inadequate Security Measures (Article 32):
- Failing to protect data, leading to breaches or leaks.
- Happens due to poor security practices like outdated software.
GDPR Fines Across Industries
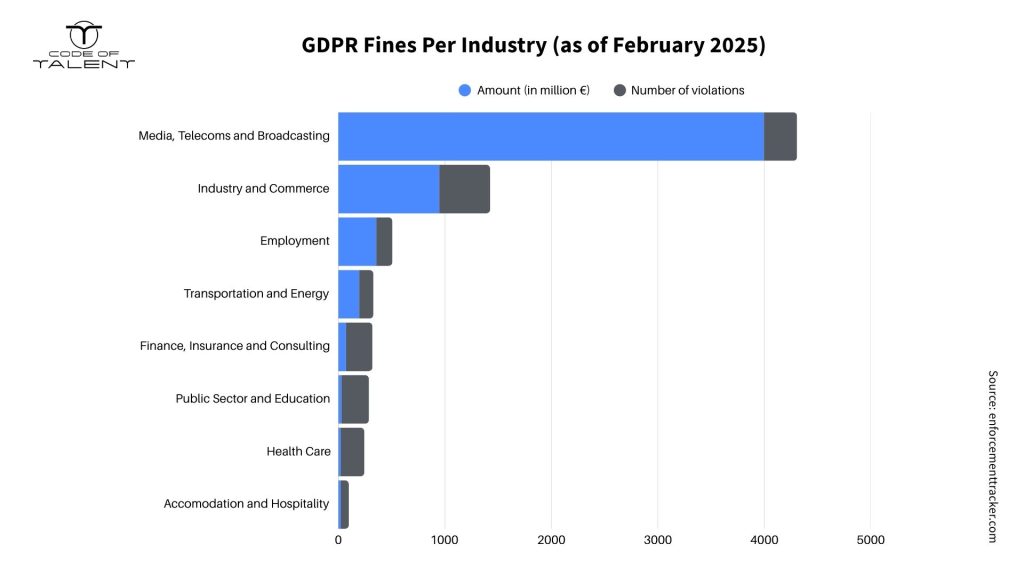
As highlighted in the chart above, the media and commerce industries have faced the highest GDPR fines, with penalties reaching billions of euros. However, other sectors such as HR, transportation, finance, public services, and healthcare have also found themselves under GDPR’s radar.
In this section, we’ll explore some of the most notable historic GDPR fines across these industries.
1. Media, Telecoms and Broadcasting
- Company: Meta (Facebook)
- Fine amount: €1.2 billion
- Reason for violation: Unlawful transfer of personal data from the EU to the US
What happened: Meta Ireland was fined a record €1.2 billion by Ireland’s Data Protection Commission for continuing to transfer user data from the EU to the US, despite the Schrems II judgment. Schrems II invalidated the Privacy Shield framework and found that US laws didn’t provide adequate protection for EU citizens’ data. Meta was ordered to suspend these transfers within five months. This is, to this date, the highest GDPR fine against a company.
What we can learn: Even tech giants aren’t immune to GDPR scrutiny. This case reminds us that when it comes to handling personal data, businesses need to stay on top of changing laws and make sure their practices protect people’s privacy.
2. Industry and Commerce
- Company: Amazon
- Fine amount: €746 million
- Reason for violation: Lack of valid consent for data processing
What happened: Amazon processed personal data without proper consent, after over 10,000 individuals in France complained that the company did not obtain explicit, informed permission. Although Amazon disclosed how it used data, its consent process didn’t meet GDPR requirements. A Luxembourg court later dismissed the company’s appeal, upholding the fine.
What we can learn: Transparency alone isn’t enough. Businesses must also get clear, informed consent before processing personal data. This case shows that vague or passive consent mechanisms can lead to major penalties under GDPR.
3. Employment/HR
- Company: H&M Hennes & Mauritz Online Shop (fashion retailer in Germany)
- Fine amount: €35 Million
- Reason for violation: Spying on employees
What happened: The company received the fine after its managers kept “secret dossiers” on staff, including sensitive data like health status, family matters, and religious beliefs. The information was collected through return-to-work interviews and gossip, then used to make HR decisions.
What we can learn: Employers must tread carefully when handling employee data. Internal surveillance and informal data collection can easily cross into illegal territory.
4. Transportation
- Company: Uber
- Fine amount: €290 Million
- Reason for violation: Transferring driver data to the US
What happened: The Dutch Data Protection Authority fined Uber for transferring the personal data of European taxi drivers to the US without adequate safeguards. The transfers lacked the necessary legal and technical protections mandated under GDPR.
What we can learn: GDPR doesn’t just apply to customer data—employee and contractor data is equally protected. Businesses must establish proper legal mechanisms before moving data outside the EU.
5. Banking
- Company: CaixaBank
- Fine amount: €6 Million
- Reason for violation: Forced consent in privacy policies
What happened: Spanish bank CaixaBank required customers to accept a new privacy policy that allowed sharing of personal data across all companies in its group. However, the customers couldn’t decline signing.
What we can learn: Consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. Bundling consent with general terms and conditions isn’t GDPR-compliant.
6. Healthcare
- Company: Centric Health
- Fine amount: €460,000
- Reason for violation: Inadequate security measures
What happened: Centric Health in Ireland was fined €460,000 after a ransomware attack compromised personal data of 70,000 patients. The healthcare provider had not implemented adequate technical and organizational measures to protect this sensitive information.
What we can learn: Security is foundational under GDPR. Failing to secure personal data, especially in the healthcare sector, can lead to serious breaches and significant fines.
7. Hospitality
- Company: Hungarian Hotel
- Fine amount: €80,500
- Reason for violation: Illegal video surveillance
What happened: A hotel in Hungary was fined for its misuse of video surveillance. The cameras not only monitored hotel premises but also inadvertently recorded public spaces. On top of that, insufficient signage and disclosure meant guests and passersby weren’t adequately informed.
What we can learn: Businesses using CCTV must minimize surveillance to what is necessary and clearly inform individuals being recorded. Overreach and lack of transparency are common and costly pitfalls.
What It Means Beyond the Fine
When companies violate GDPR, the financial penalties can be steep, but they’re just one part of the damage. The real cost often lies in what follows: broken trust, disrupted operations, and long-term financial fallout.
- Reputation loss: A Forbes article reports that 75% of consumers would cut ties with a company that mishandles data. For instance, Sephora Romania’s TikTok giveaway accidentally featured a screenshot of user data, and despite quickly deleting the post, the mistake damaged the brand’s reputation for weeks.
- Lawsuits and legal issues: Violations can lead to shareholder lawsuits and investor panic. Facebook, facing GDPR scrutiny, saw its stock drop and was sued by shareholders for misleading them about data protection and financial risks.
- Operational shutdown: GDPR can force companies to rethink their business model. For instance, Verve, a U.S. mobile ad company, pulled out of Europe because its reliance on location data made compliance too costly and complicated.
GDPR Training for Employees: What’s Out and What’s In
Now that we’ve explored the real impact of GDPR non-compliance, let’s focus on how to prevent these pitfalls. While we won’t dive into the technical or legal aspects, we’ll look at how training employees can help avoid these mistakes and what works and what doesn’t work anymore in data protection training.
Building a strong learning foundation is key to creating a safer, more compliant environment.
What’s Out: Passive Learning
“Mandatory” doesn’t always mean “effective.” While it’s common to require employees to complete GDPR training, just ticking the box doesn’t guarantee that learning sticks. Employees often view HR-assigned GDPR training as a chore, pushing it aside in favor of other tasks. As a result, they end up checking boxes, skipping through presentations, or mentally tuning out, which leads to ineffective learning.
Passive learning methods, like reading PDFs, often fail to prepare employees for real-world scenarios because of the way they’re delivered. Companies need to rethink their approach to GDPR training.
What’s In: Active Learning
To build a more effective GDPR training program, it’s essential to embrace more active, engaging techniques. Active learning encourages participation, application, and deeper understanding, ultimately resulting in better retention and stronger compliance in the workplace.
Here’s how modern training approaches can make a difference:
- Microlearning (bite-sized, role-specific modules): Breaks down content into short, focused modules tailored to specific roles, reducing information overload.
- Interactive feedback: Provide immediate, real-time feedback on exercises and quizzes to help employees understand and correct mistakes on the spot.
- Gamification: Turn training into a game with rewards, challenges, and leaderboards.
- Peer collaboration: People learn better together and from one another.
- Mobile accessibility and real-time learning: Allow employees to access training content on mobile devices anytime, anywhere.
- Simulated scenarios for hands-on practice: Simulate real-world GDPR scenarios to provide employees with practical experience.
Best Practices for GDPR Training for Employees
Let’s look at the best approaches for training employees in GDPR or data protection.
Core GDPR Principles to Teach
For a GDPR training program to be truly effective, employees must understand core data protection principles that guide how personal data should be handled, stored, and protected across any organization.
Employees should be familiar with these 7 GDPR pillars:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Employees must ensure data is processed legally and individuals are informed about its use.
- Purpose limitation: Data should only be used for its intended purpose, and employees must avoid using it for anything else.
- Data minimization: Only collect the data necessary for the task to reduce risk.
- Accuracy: Employees must correct inaccurate data and keep it up to date.
- Storage limitation: Data should be kept only as long as necessary, not indefinitely.
- Integrity and confidentiality: Employees must protect data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Accountability: Employees play a role in ensuring compliance and assisting with audits and monitoring.
What to Teach During GDPR Training for Employees
Clear, actionable steps for employees to follow can prevent common GDPR missteps. It’s essential that employees not only understand the regulations but know what specific actions they need to take.
1. What is GDPR and why it matters
This is the theory-based part of the training: legal overview, understanding core principles, and evaluating risks.
Make it engaging: Consider using microlearning to break down complex concepts into digestible pieces. Additionally, with the help of AI, microlearning platforms also transform long GDPR documents into short and engaging training content. Simply upload your company’s data protection materials, and AI will condense it into sessions no longer than 10 minutes.
Example: Create a 5-minute video or interactive module on “What GDPR Protects and Why It Matters,” followed by quick quizzes or infographics.
2. Department-specific risks and responsibilities
Every team handles data differently. What’s risky in healthcare might not apply to IT or customer service. That’s why GDPR training should be tailored to reflect each department’s day-to-day realities.
Make it engaging: Use interactive role-based scenarios that simulate real decisions employees make in their specific roles.
Example: Simulate a customer service scenario responding to a data deletion request. Use different tones (friendly, angry, disappointed, or confused), so employees can practice how to remain respectful and GDPR-compliant no matter the mood on the other end.
3. Obtaining consent
Consent is a core requirement under GDPR, and employees must know how to ask for it properly, especially when sensitive data is involved.
Make it engaging: Use collaborative learning to apply theoretical knowledge through real-world practice. First, walk employees through the legal framework (what qualifies as valid consent, when it’s required, and the needed documentation), then move on to role-play exercises reviewed by colleagues.
Example: Create a simulation where employees request consent from colleagues in different scenarios. Have colleagues evaluate whether the request was clear, specific, and lawful. This is especially powerful in healthcare, finance, and education, where consent collection is routine but highly regulated.
4. Identify and report potential data breaches
GDPR requires organizations to report personal data breaches within 72 hours. Employees need to recognize red flags early and know how to respond without hesitation.
Make it engaging: Use real-world breach scenarios to teach incident response.
Example: Split employees into small groups and give them a breach scenario. Each team must identify what went wrong, how it should be reported, and how to mitigate future risk. This exercise is especially useful for fast-paced industries like media, telecom, or IT.
5. Common workplace data privacy slips
Data mishandling often happens not in big hacks, but in everyday actions like forwarding the wrong email or leaving documents unsecured.
Make it engaging: Use visual learning to highlight frequent mistakes. Infographics, interactive videos, and drag-and-drop quizzes can teach employees to spot privacy issues in familiar contexts.
Example: Design visuals showing poor vs. proper data handling: e.g., someone leaving a printed list of client emails in a shared space, or sending personal info over an unencrypted chat app.
6. Stay up to date on latest developments
GDPR rules, interpretations, and best practices evolve constantly. Keeping employees informed ensures ongoing compliance and reduces the risk of outdated behavior.
Make it engaging: Use just-in-time training platforms and mobile-friendly apps that deliver timely GDPR updates as part of daily workflows. These tools allow for quick refreshers without interrupting work.
Example: A pharma sales rep heading into a doctor’s office could complete a 5-minute refresher module on GDPR guidelines before the meeting. The same approach works well in other highly regulated industries like finance, insurance, and tech.
All Features Into One Platform
With GDPR fines climbing into the billions, companies can’t afford to take shortcuts when it comes to data protection. The cost of failing goes far beyond money. It damages reputations, invites legal trouble, and can even threaten a business’s existence. That’s why GDPR training for employees is no longer optional but essential.
Code of Talent offers a practical solution for delivering an engaging and effective GDPR training. Using scenario-based simulations, real-time feedback, and job-related customized learning journeys, employees absorb the “why” behind the rules, not just the “what.”
Don’t wait for a breach to take action. Invest in GDPR training for employees today with Code of Talent and empower your team to protect your business and your customers!
Cover Photo: Freepik





