The dream of any business executive, HR manager, or L&D rep is for a new hire to become productive in less than one month: finish onboarding in the first few weeks and bring value right after. However, this is almost impossible, as studies and expert opinions suggest. A survey found that most managers don’t believe employees reach full productivity within the first six months. Another study revealed that, on average, it takes eight months for new employees to become fully productive. Some companies even reported that it takes over a year. Despite this, 58% of companies don’t even measure time to productivity, leaving this critical metric largely invisible.
The issue isn’t just about employees needing time to adjust; it’s about how organizations support them. Structured onboarding, mentoring, and better workplace support can make all the difference in fixing the sluggish time to productivity.
This article explores the main reasons behind a slow time to productivity and provides 20 practical tips to break through that barrier.
What Is Time to Productivity?
Time to productivity is a key recruitment metric that measures the time between a new hire’s first days of work until they become fully productive and bring value to the business. This includes demonstrating that they are skilled and prepared enough to complete the job independently.
However, we need to make a distinction between time to productivity and time to proficiency—related but distinct metrics. Time to productivity refers to achieving expected performance levels, while time to proficiency is about mastering complex skills and excelling beyond standard expectations.
Factors Impacting Time to Productivity
As with any business metric, several factors influence time to productivity. Below are five of the most critical variables.
Quality of Onboarding and Training
Onboarding dictates if an employee will thrive or not at a company. At its worst, poor onboarding leads to early resignations, turning strategies for employee independence into desperate efforts to retain them. Over a quarter of employees are willing to quit within the first 90 days due to disappointing onboarding, and according to Yahoo Finance, 80% of those who experience poor onboarding plan to leave. The problem with turnover isn’t just about lost employees. It also comes with additional costs from restarting the hiring and training processes. In fact, losing an employee can cost anywhere from tens of thousands of dollars to twice their annual salary.
In the best-case scenario, a strong onboarding and training program lays the foundation for a successful collaboration between employee and employer, and most importantly, sets the path to productivity. Providing the right support, relevant training, clear milestones, and a structured induction program leads to better results from the get-go.
Previous Experience and Transferable Skills
At first glance, these factors may seem straightforward: the more experience and relevant skills a new hire has, the easier their transition. If they come from a similar role or industry, adapting to new procedures and responsibilities is usually smoother than for someone switching careers or with no experience at all.
However, experience isn’t always an advantage. Some highly experienced professionals may struggle to adapt to new environments, especially if they feel overqualified for the role or find it challenging to unlearn old habits. Striking the right balance between relevant experience and adaptability is key to reaching productivity in a timely manner.
Use of Technology and Tools
Integrating technology and digital tools into the workplace significantly reduces the time employees need to reach full productivity. Automating repetitive tasks, facilitating communication, and streamlining processes are some of the benefits that technology brings within the onboarding process.
However, outdated or inefficient technology can have the opposite effect. Small businesses, for example, lose over 98 hours per year due to misfiring tech, the equivalent of 12 working days. In contrast, business owners estimate a 40% productivity boost if their technology ran more smoothly.
Organizational Culture and Support
A strong workplace culture directly influences productivity—companies that invest in culture see a 32% boost in employee productivity and a 20% increase in sales, according to Harvard Business Review. Humans are naturally social, and workplace relationships can make or break an employee’s experience.
For new hires, guidance, patience, and support from colleagues are essential to feel accepted and integrated within the company’s environment. When they are ignored, judged, or rushed, they are more likely to make mistakes, struggle with tasks, or even leave in search of a more supportive environment.
Managerial Support and Feedback
Poor management costs U.S. companies at least $960 billion per year. This number does not come as a surprise as many people quit their jobs because of toxic bosses. For new hires, managers play a crucial role in shaping their experience: introducing them to company culture, facilitating communication, and providing early guidance.
According to Forbes, a good manager helps employees become productive faster by guiding them, correcting mistakes, and keeping them motivated. Managers who are well-trained in onboarding and employee development are key to reducing time to productivity.
20 Tips to Improve Time to Productivity
Keeping in mind the previously mentioned factors, here are 20 practical tips to improve time to productivity.
1. Structured Onboarding Programs
Description: Develop a comprehensive onboarding journey that clearly outlines company culture, role expectations, and key procedures.
Added tip: Create a 30-60-90 day roadmap with clear milestones, check-ins, and defined success metrics.
2. Cohort-Based Customized Training Plans
Description: Pair new hires into cohorts and provide training simultaneously to encourage mutual support and collaboration. Tailor training programs specifically to the cohort’s needs.
Added tip: Structure role-specific training tracks within each cohort, incorporating peer mentoring, group problem-solving activities, and real-world simulations for efficiency.
3. Mentorship Assignments
Description: Pair new employees with experienced mentors to guide them through challenges and provide ongoing support.
Added tip: Give mentors access to the new hire’s training materials and progress reports for them to provide targeted feedback, track development, and offer personalized guidance.
4. Clear Overall Performance Goals
Description: Establish performance goals for new hires and communicate them clearly from the beginning. Use SMART (short, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timely) goals for efficiency and accuracy.
Added tip: Incorporate these goals in a training platform to track their progress and measure essential training KPIs such as engagement, completion rates, and success scores.
5. Regular Feedback Loops
Description: Implement frequent check-ins between new hires and manager/mentor to provide constructive feedback and address concerns.
Added tip: Encourage two-way feedback so employees can share their own experiences and suggestions.
6. Access to Necessary Tools
Description: Provide new hires with access to all required technology and resources before their first day. This includes purchasing and setting up equipment, configuring passwords and software access, and testing all tools in advance.
Added tip: Create an IT and resource checklist to ensure that a new hire’s first day or week goes without tech malfunctions.
7. Interactive Learning Modules
Description: Use engaging and interactive training materials to improve learning retention and engagement during the training phase of onboarding.
Added tip: Use gamification elements (e.g., quizzes, challenges) to make training more engaging.
8. Cross-Departmental Exposure
Description: Allow new hires to experience different departments to understand other company operations and broaden their skills.
Added tip: Implement job shadowing opportunities so employees can see different roles in action.
9. Soft Skills Training
Description: Provide training on essential soft skills such as effective communication, time management, and problem-solving.
Added tip: Use scenario-based training in a risk-free environment, such as microlearning platforms, to reinforce soft skills in real-world contexts. For example, in the medical field, staff can simulate patient conversations on sensitive topics on a microlearning platform.
10. Compliance Training
Description: Prioritize compliance, risk, and safety training during onboarding so that new hires understand industry regulations, company policies, and ethical standards. A strong program reduces risks and costly mistakes.
Added tip: Compliance training is usually deemed dull and boring by employees. Use videos, case studies, and interactive content to make training more engaging. Bonus points: invite real-life experts, such as safety officers, firefighters, police, or industry professionals, to share insights on workplace risks and best practices.
11. Encourage Questions
Description: Create a workplace culture where new employees feel comfortable asking questions and seeking support from both executives and colleagues.
Added tip: Create an anonymous Q&A channel where employees can ask questions without hesitation. Encourage senior employees to regularly check in on new colleagues, even if they appear self-sufficient. Most people are afraid to speak up when they don’t feel supported enough.
12. Promote Work-Life Balance
Description: Encourage practices that support mental and physical well-being. Happy and relaxed employees mean a higher chance of maximum productivity.
Added tip: Provide hybrid or remote training opportunities, wellness check-ins, and activities like ping pong, foosball, reading lunch breaks, or after-work gatherings.
13. Foster Bonding Between Direct Manager and Employee
To secure a healthy and productive relationship between a direct manager and their new team member, offer opportunities for them to bond.
Added tip: Allocate a budget for activities such as mentoring lunches, team-building games, weekly 1:1s, and informal “get-to-know-me” sessions.
14. Leverage AI in Training Efforts
Description: Integrate AI-powered tools into training programs to automate tasks, measure impact, and provide real-time feedback to new hires.
Added Tip: Use AI-driven platforms to transform long-form training materials, such as compliance guides or internal procedures, into multiple digestible modules that take no longer than 7 minutes to complete. Learners can complete these modules at their own pace and absorb large amounts of information more easily.
15. Provide Updated Training Content
Description: Ensure that training content is relevant and updated according to the employee’s role, company’s policies, and evolving business demands.
Added tip: For fast-moving industries, such as telecom, IT, or healthcare, updating training materials to reflect industry innovations is key in staying ahead of the competition. For a faster, more efficient approach, use AI to update existing training content.
16. Recognize Early Achievements
Description: Acknowledge and reward accomplishments to motivate new hires’ efforts and dedication.
Added tip: Implement a “New Hire Spotlight” feature in company meetings or newsletters.
17. Foster Team Integration
Description: Organize team-building activities to help new hires establish relationships and integrate into the company culture.
Added tip: Dedicate at least one day during onboarding to team-based games and simulations, allowing all team or department members, regardless of experience, to participate. This approach helps new hires bond with colleagues.
18. Continuous Learning Opportunities
Description: Encourage ongoing education and skill development to keep employees engaged. The ability to upskill and grow, both professionally and personally, is a key factor in job performance and long-term success.
Added Tip: Invest in modern learning technologies such as microlearning, gamification, and mobile training apps to provide flexible and engaging learning opportunities.
19. Gather Employee Feedback and Act On It
Description: Use insights from current employees to refine onboarding and training programs.
Added tip: Conduct onboarding surveys at 30, 60, and 90 days to measure effectiveness. Remember to keep surveys short and to the point. Adding clear and relevant questions, focusing on what worked well, what didn’t, and what could be improved.
20. Monitor Progress with Analytics
Description: Implement tracking systems to assess new hire performance and identify areas needing support.
Added tip: Microlearning platforms can easily track training KPIs and offer insights into the program’s effectiveness.
A Proven Solution for an Improved Time to Productivity
Reducing time to productivity isn’t just about expecting employees to work harder—it’s about giving them the right tools, training, and support to succeed.
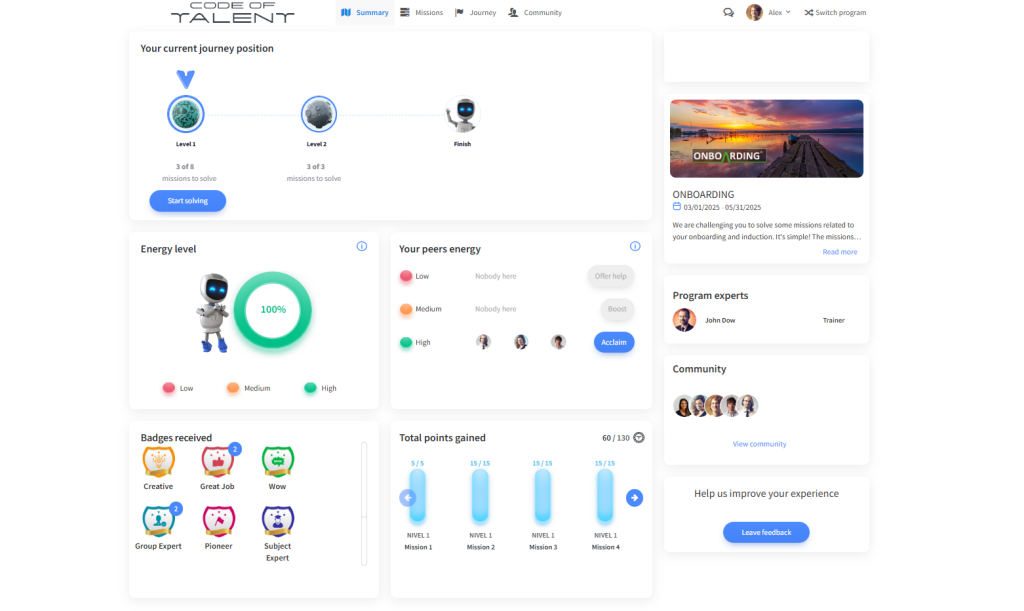
Code of Talent helps companies solve time-to-productivity challenges by offering a digital, interactive microlearning platform. Some of its features contain:
- Bite-sized content for better information retention
- Collaborative learning opportunities
- Insights and training metrics for tracking progress
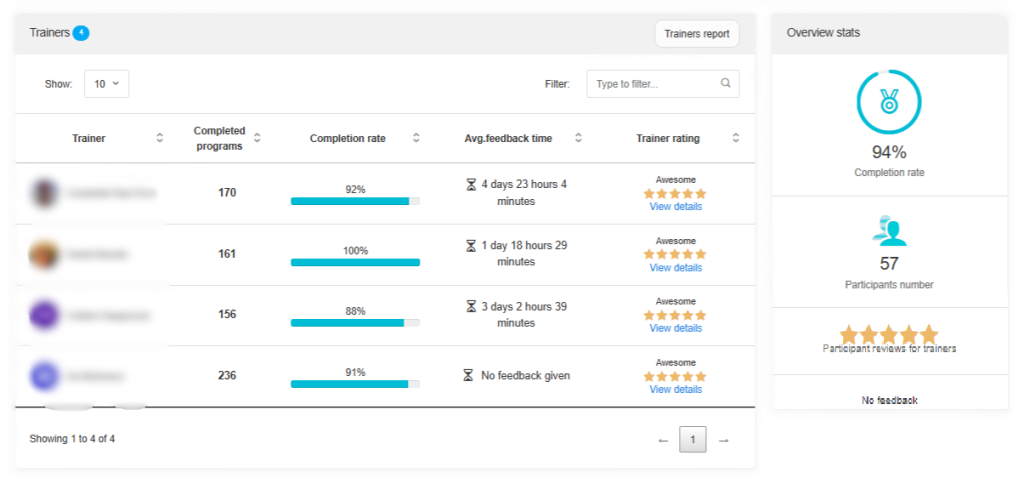
- Monitoring by managers, trainers, mentors, or leadership
- Gamification
- Interactive content such as real-life scenarios, quizzes, story-time assessments, and discussions
Time to Productivity Success Story
After incorporating Code of Talent into their onboarding and training processes, a commercial bank reduced the time employees needed to reach full performance by 50%, from 6 months to just 3 months.
Code of Talent offers an innovative approach to improving time to productivity, making learning more efficient and impactful. It’s time to rethink onboarding and focus on getting employees up to speed faster and smarter. Create a free onboarding journey using Code of Talent’s free trial and see how easy it is to improve time to productivity from the very beginning!
Cover photo: Freepik





